A bus is a collection of common signal lines used for transmitting information and enabling communication between modules or devices. It serves as a signal carrier or public channel that, under the control of a master device, accurately transmits information from a sending device to a receiving device.
EtherCAT (Ethernet Control Automation Technology) is an open-architecture fieldbus system that leverages Ethernet technology. The "CAT" in EtherCAT stands for Control Automation Technology. It was originally developed by Beckhoff Automation GmbH in Germany.
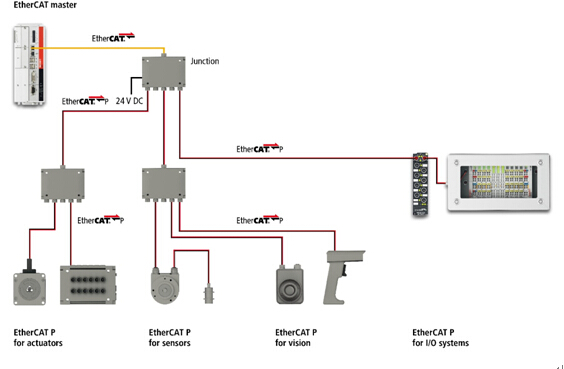
EtherCAT sets new benchmarks for real-time performance and topology flexibility, while meeting or even reducing the cost of traditional fieldbuses. It offers high-precision device synchronization, optional cable redundancy, and functional safety protocols (SIL3).
In terms of topology, EtherCAT supports almost all configurations, including line, tree, and star topologies. This means that the line structure commonly used in fieldbuses can also be employed in Ethernet-based systems. The combination of bus and branch structures is particularly advantageous for system wiring, as all interfaces are located on the coupler, eliminating the need for additional switches. However, the traditional switch-based star Ethernet topology is also supported.

